How Do You Map B2B SaaS Customer Journey?
Mapping a B2B SaaS customer journey is a complex, multi-stage process. You begin it by focusing on what your business wants to achieve, and with every stage, you shift your focus more and more on the needs, pain points, and interactions of your customer base.
Having worked with many B2B SaaS companies over the years, we’ve established the following mapping sequence as the most effective:
- Define Objectives: DB SaaS customer journey map is always to define clear and specific strategic goals – Do you aim to boost user retention, improve conversion rates, or enhance the onboarding experience? Answering this question will guide the entire mapping process, ensuring that you focus on the areas that matter most to your business specifically.
- Identify Customer Personas: Customer personas should represent different segments of your user base and play a pivotal role in understanding your target audience. Ideally, they should have as many details as possible, including characteristics such as job roles, pain points, and objectives.
- Gather Customer Data: Both quantitative and qualitative data will provide the empirical basis for understanding how customers interact with your product at each stage of their journey. While mapping out your customer journey in B2B SaaS, leverage the insights collected through website analytics, surveys, support interactions, and user interviews.
- Create Customer Journey Stages: At this stage, you divide your customer journey into well-defined stages; and while the specific stages may vary depending on your business model, common ones for B2B SaaS include awareness, evaluation, acquisition, activation, retention, expansion, referral and revenue (we’ll go into detail on these stages in the later section).
- Identify Touchpoints: Each stage of the SaaS buyer journey is punctuated by touchpoints where customers interact with your brand. These touchpoints can be both digital or offline: digital ones may include website visits, email communication, or app usage, while offline touchpoints could involve attending webinars or engaging with sales representatives.
- Map Customer Emotions and Pain Points: An aspect that is sometimes overlooked, the emotional journey of customers is another critical part of mapping. Understanding customer goals, fears, and expectations at each touchpoint is key to crafting an emotionally resonant customer experience.
- Iterate and Refine: When the customer journey mapping is done, remember that it’s never really “done” – it is an iterative process. Continuously collecting data and feedback will allow you to refine your maps as customer preferences and market dynamics evolve. This way, through the regular revisiting and updating of the maps you make sure that your strategies remain relevant and effective over time.
Importance Of Customer Journey Maps For B2B SaaS Companies
At its core, B2B SaaS customer journey mapping produces a lot of valuable output: gives you a clear vision of your customer personas, how they interact with your business as well as a blueprint on how to improve their experience with you.
To provide more detail, we can say from experience that:
- Comprehensive Process Understanding: Customer journey mapping visualizes the entire customer’s path from awareness to adoption and provides invaluable insights into how your entire sales and marketing processes work. For instance, seeing when potential customers first become aware of your brand can allow you to create targeted content and campaigns, ensuring that their messaging resonates with the personas. Additionally, a comprehensive understanding of the SaaS customer lifecycle is instrumental in aligning internal teams, from marketing and sales to product development and customer support. When everyone shares a clear vision of the customer’s journey, collaboration becomes smoother, and decision-making becomes more customer-centric.
- Deep Insights On Customers: If done right, a B2B SaaS customer journey map will go beyond basic demographic data and will let you delve into the motivations, pain points, and emotions that drive customer decisions. Armed with this information, you can then proactively address various issues, whether through product improvements, better customer support, or clearer communication. It’s also worth noting that when your sales and marketing teams start thinking as a customer, they will be likely to develop a level of empathy, which is essential for building lasting customer relationships. It allows them to communicate more authentically and demonstrate a genuine commitment to solving customer problems.
- Enhanced User Experience: By breaking down the SaaS customer journey stages into individual touchpoints and interactions, you can focus on improving each element, which often results in an overall more satisfying user experience. If a map reveals that customers often struggle during the onboarding process, you can invest efforts in redesigning the experience to make it more user-friendly. This can involve simplifying registration steps, providing clearer instructions, or offering in-app tutorials. Furthermore, identifying pain points will help you allocate resources to areas that have the most significant impact on user satisfaction, resulting in higher retention rates and customer loyalty.
- Improved Customer Engagement: Maps also offer opportunities to engage customers effectively; we’ve already mentioned that you can create compelling content that addresses common pain points or provides solutions to common challenges. But you should also keep in mind that post-purchase engagement is equally crucial – providing tutorials, training resources, or access to dedicated customer support during this phase can significantly boost customer engagement. Not to mention, these maps help with monitoring customer interactions and sentiment throughout the journey, allowing you to identify certain trends, spot potential issues, and make real-time adjustments to your engagement strategies.
- Optimization Guide: At their most basic, customer journey maps serve as optimization guides for B2B SaaS companies, directing them toward refining their products – instead of spreading resources evenly across all customer touchpoints, you can focus your efforts where they will have the most significant impact on customer satisfaction and retention. Overall, by analyzing moments of high satisfaction along the journey, you can identify what resonates with customers and replicate these positive experiences.
- Adaptability: Lastly, B2B customer journey touchpoint mapping is essential for adapting to the ever-changing environment of SaaS. By regularly revisiting and updating them, you can ensure that your strategies remain aligned with evolving customer expectations and industry trends. For example, if there’s a change in the customer-preferred communication channel, the maps may be adjusted to reflect this shift. On top of that, maps encourage a culture of continuous improvement, motivating teams to explore new strategies, experiment with different approaches, and innovate based on customer insights.
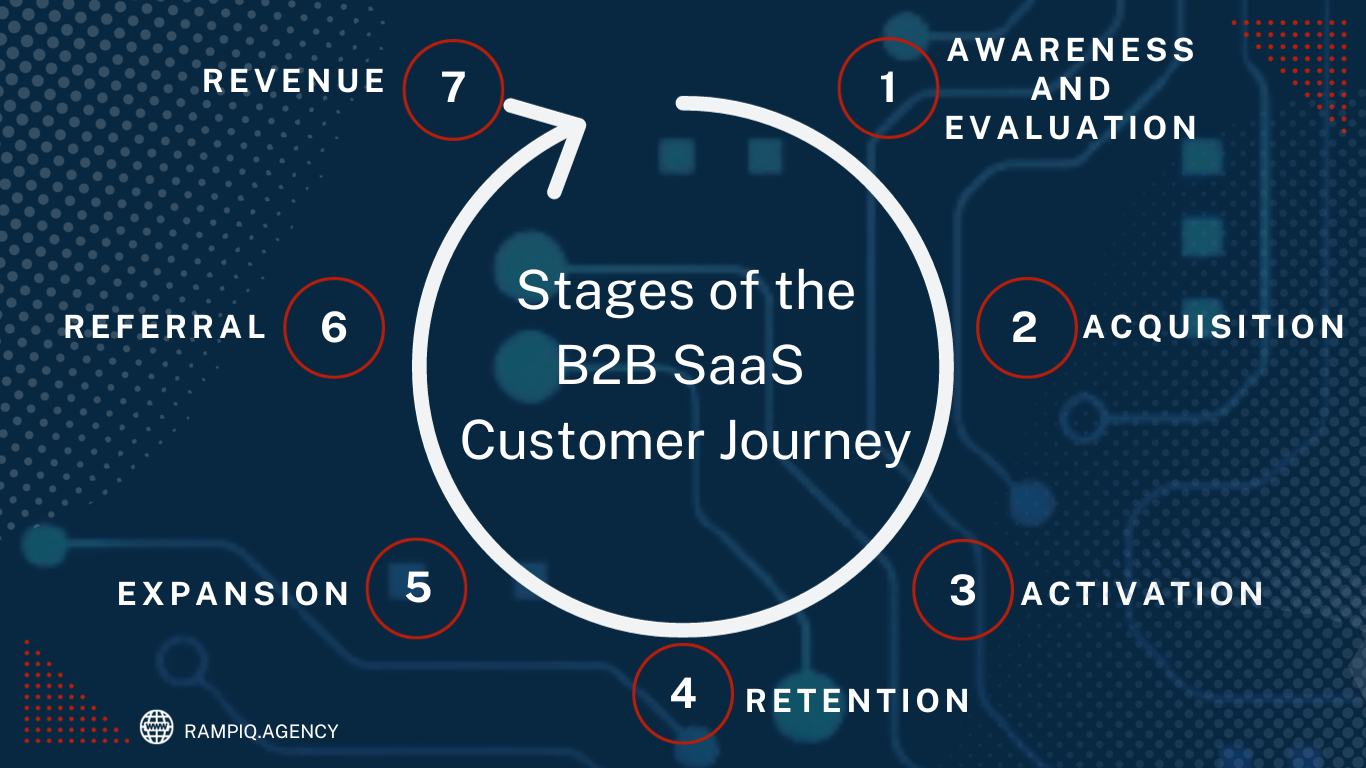
Stages Of The B2B SaaS Customer Journey
We know that B2B SaaS customer decision journeys differ from more traditional funnels, but even within B2B SaaS itself, there are different types of maps that offer different names and meanings for each stage. The following sequence is the most comprehensive and accurate depiction:
- Awareness and Evaluation
- Acquisition
- Activation
- Retention
- Expansion
- Referral
- Revenue
1. Awareness and evaluation
This stage marks the beginning of the B2B SaaS customer journey – potential customers get to know about your SaaS solution during their research on which product can satisfy their business challenge or need. This is also when they actively evaluate their options, seeking a solution that best aligns with their requirements.
To capture their attention, it’s recommended to invest in effective marketing strategies, such as producing educational content that addresses specific pain points or utilizing targeted paid ad campaigns to reach broad audiences within your specific niche or industry.
2. Acquisition
In this phase, prospects turn into customers – they have moved beyond evaluation and have decided to commit to your SaaS solution. So, this is the stage when the purchase actually takes place; that’s why ensuring a frictionless and user-friendly acquisition experience is very important.
Your sales teams should engage with leads, provide relevant product information, and address questions or concerns. Also make sure to use personalized email campaigns to nurture those leads, offering them customized solutions.
3. Activation
Once customers have acquired your SaaS product, the activation stage begins. This is where users are setting up their accounts, configuring the software, and starting to explore its features.
Remember to provide your users with easy onboarding, high-quality tutorials, and responsive customer support.
4. Retention
This stage focuses on maintaining long-term customer relationships, with businesses closely monitoring user engagement and satisfaction levels.
You should offer responsive customer support to address questions and concerns promptly, demonstrating your commitment; as well as regularly educating users about your product’s features, updates, and best practices to encourage engagement.
5. Expansion
As customers become more familiar with your product, there will appear opportunities for expansion, which involves offering additional services or features as valuable upgrades.
This is where your team needs to continually communicate the value your product provides,
and identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell additional plans.
6. Referral
The referral stage leverages satisfied customers to become advocates for your SaaS product, which can be a powerful source of new acquisitions.
To stimulate that, you can and should implement advocacy programs that reward and recognize loyal customers for referrals and testimonials. Another good practice is to foster user communities or forums where customers can share insights, best practices, and success stories with one another.
7. Revenue
The last, revenue stage encompasses all the financial aspects of the customer journey in B2B – ongoing subscription renewals, optimizing pricing strategies, and strategically managing upselling and cross-selling initiatives.
Make sure to assign dedicated account managers to nurture key accounts and continuously analyze user behavior to identify opportunities for upselling.
Map Your SaaS Customer Journey
We’ll turn your real funnel stages and touchpoints into a practical journey map tied to concrete SEO and content actions.
Map My Journey
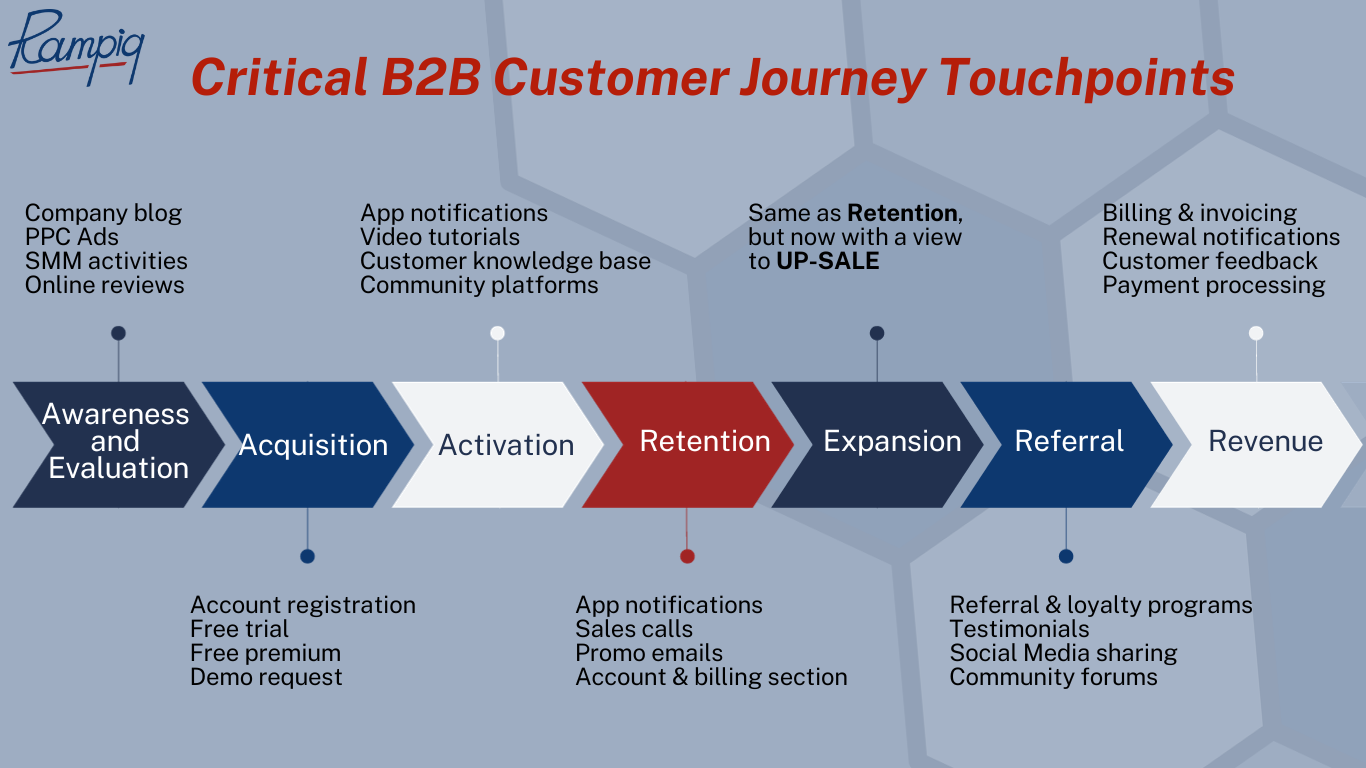
Critical B2B Customer Journey Touchpoints
Each B2B customer journey stage is characterized by how exactly a potential user interacts with your business – and all such interactions are commonly referred to as touchpoints. In this section, we’ll mark the most common and important B2B customer journey touchpoints for each stage:
- Awareness and Evaluation – company blog, PPC ads, SMM activities, word-of-mouth advertising, online reviews/testimonials, influencer marketing campaigns, organic search results, and webinars.
- Acquisition – account registration, free trial, free premium, demo request, onboarding emails.
- Activation – app notifications, video tutorials, customer knowledge base, emails with tips on advanced use, and community platforms.
- Retention – app notifications, sales calls, subscription purchase reminders, promo emails, account and billing section.
- Expansion – same as retention, but now with a view to not just sell, but up-sell.
- Referral – referral and loyalty programs, testimonials, social media sharing, community forums.
- Revenue – billing and invoicing, renewal notifications, customer feedback, payment processing, and account management.
B2B SaaS Customer Journey Example: Product-led SaaS
Product-led SaaS implies that your company’s entire growth relies purely on product usage, i.e. in what ways and how much users interact with your product.. According to this approach, there is hardly or no direct sales involved (sales call, request a demo); instead, the in-product experiences are the main drivers for growth.
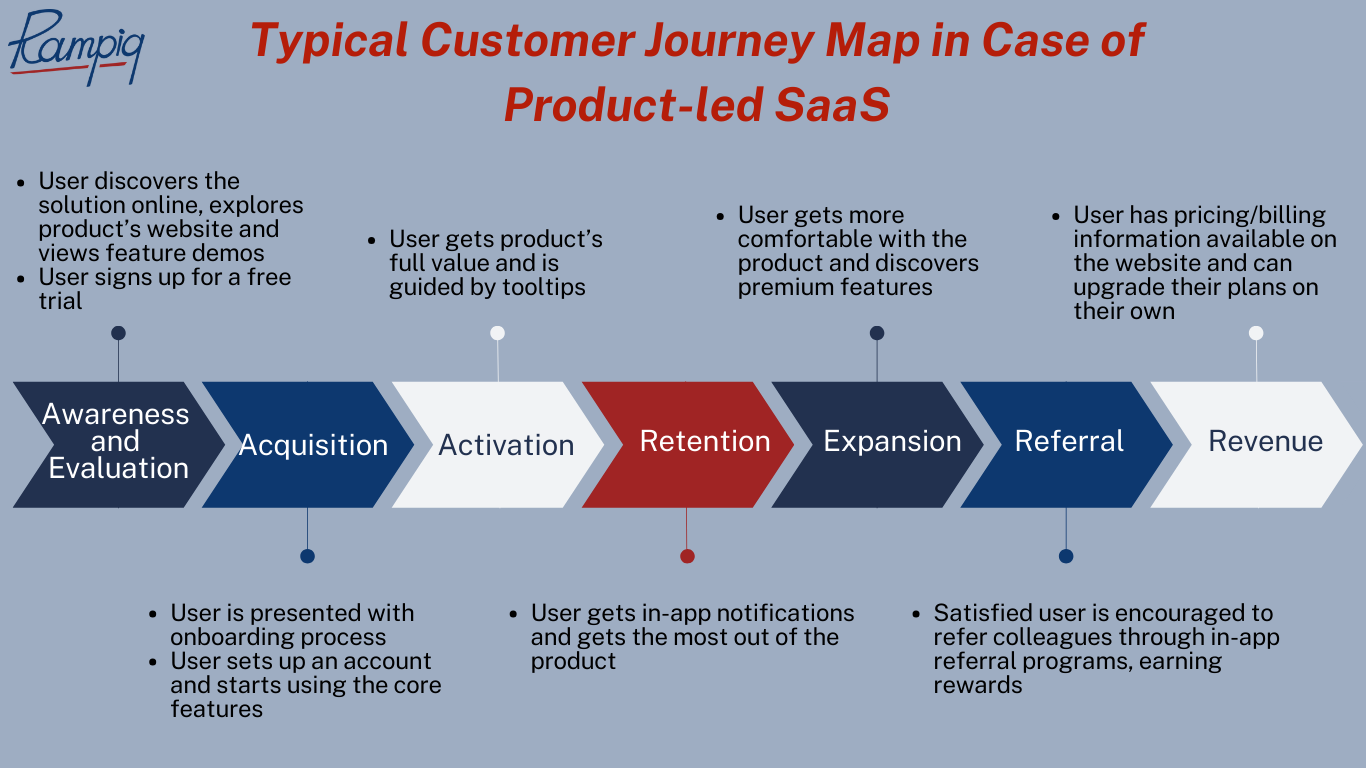
A typical customer journey map in the case of product-led SaaS may look like this:
- Awareness and Evaluation: Customers discover the solution through online searches or content marketing; then start exploring the product’s website, view feature demos, and engage with online guides and tutorials. This is also where users should be encouraged to sign up for a free trial with minimal friction.
- Acquisition: After signing up, users are presented with a guided onboarding process, making it easy to set up their accounts and start using the core features. The product-led approach will allow users to explore and experiment with the software on their own, without requiring direct sales interactions.
- Activation: Users are prompted to complete specific actions or tasks within the product to get its full value; normally guided by interactive tooltips and in-app notifications.
- Retention: Here, customer engagement is maintained through automated email campaigns and in-app notifications that highlight new features and provide tips for getting the most out of the product.
- Expansion: As users get more comfortable with the product, they are subtly encouraged to discover premium features and subscription upgrades if needed.
- Referral: Satisfied users are encouraged to refer colleagues and friends through in-app referral programs, earning rewards.
- Revenue: At this stage having your pricing and billing information readily available on the website is the most important so that users can upgrade their plans on their own.
B2B SaaS Customer Journey Example: Sales-driven SaaS
Sales-driven SaaS means your customers can only purchase your product after at least one human sales interaction. Where product-led SaaS focuses on free trials, in sales-led organizations events like sales calls are the foundation. The goal of this approach is to hold talks with potential users, where you will show them the value of your product.
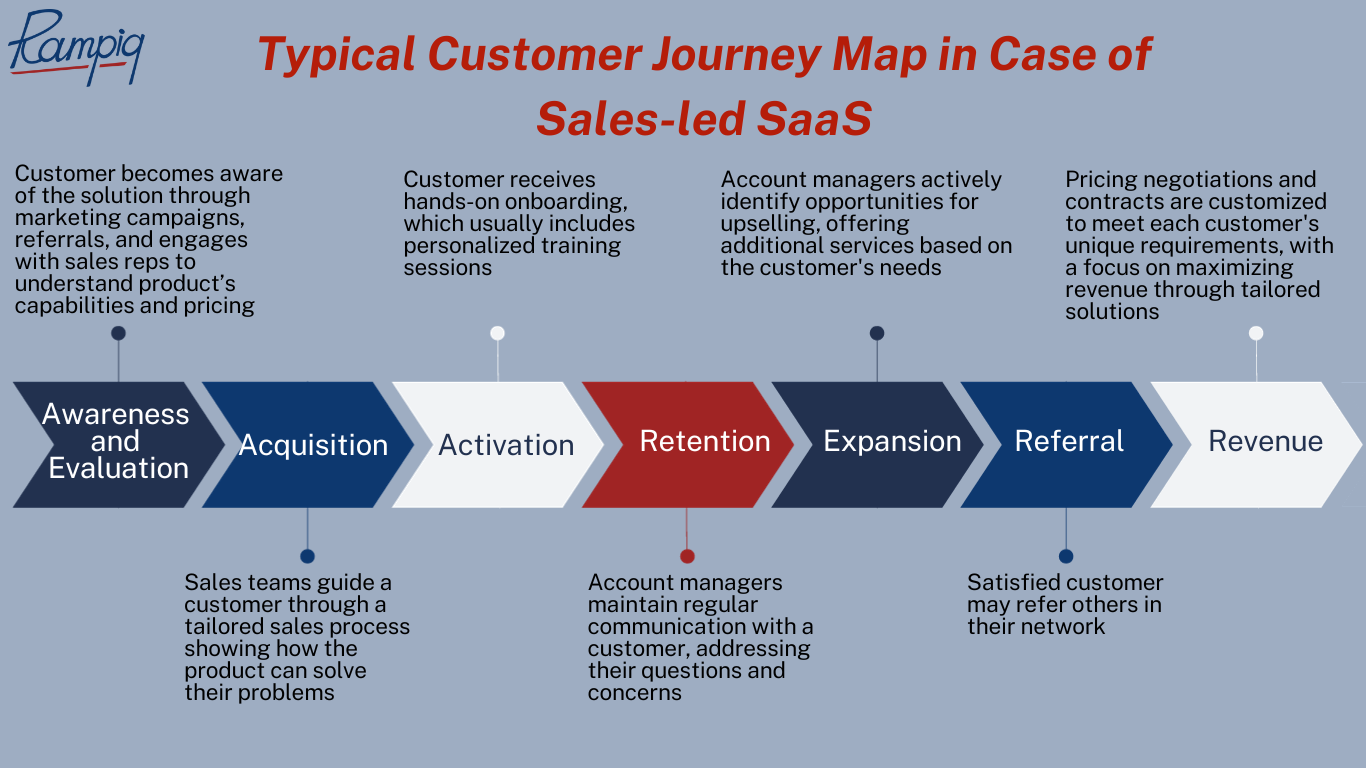
A typical customer journey map in the case of sales-led SaaS may look like this:
- Awareness and Evaluation: Customers become aware of the solution through marketing campaigns or referrals, and then engage with sales reps through scheduled calls, demos, and meetings to understand the product’s capabilities, pricing, and suitability for their personal needs.
- Acquisition: Sales teams guide customers through a tailored sales process, addressing specific pain points and showcasing how the product can solve their challenges.
- Activation: Customers receive hands-on onboarding, which usually includes personalized training sessions to make sure they are comfortable using the product.
- Retention: Account managers or customer success teams maintain regular communication with customers, addressing their questions and concerns.
- Expansion: Account managers actively identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling, offering additional services or features based on the customer’s needs.
- Referral: Satisfied customers may refer others in their network, however, referrals are often generated through direct sales relationships.
- Revenue: Pricing negotiations and contracts here are customized to meet each customer’s unique requirements, with a focus on maximizing revenue through tailored solutions.