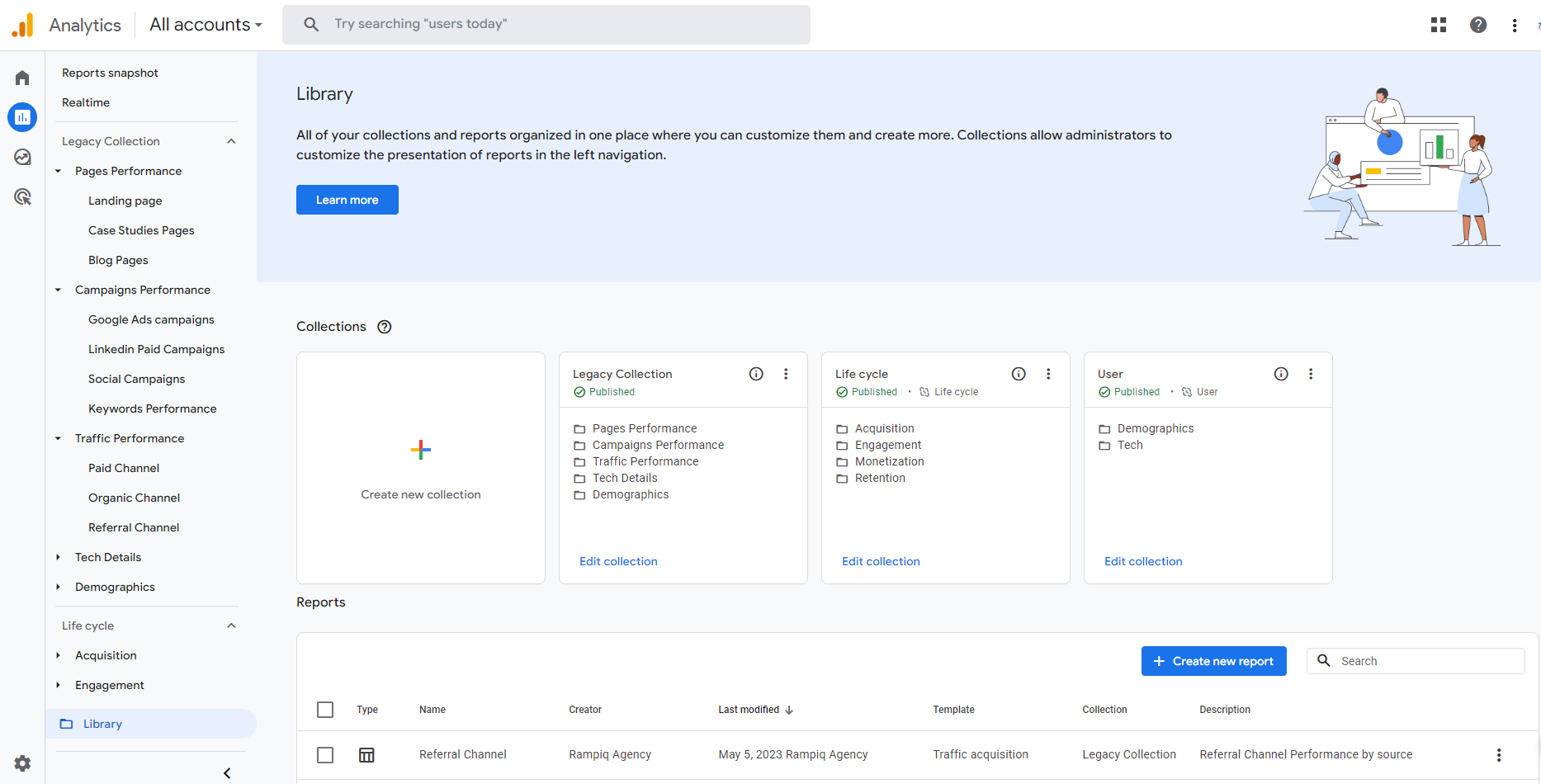
Here’s our step-by-step GA4 migration checklist for SaaS companies:

GA4 migration checklist
Step 1. Prepare a Migration Plan
We highly recommend documenting all events, goals, and other important settings that you have in Universal Analytics in a spreadsheet or a migration document where you can get the full migration scope and then run the post-migration QA check.
It is also important to double-check user permissions and make sure your key stakeholders get access to GA4 reports.
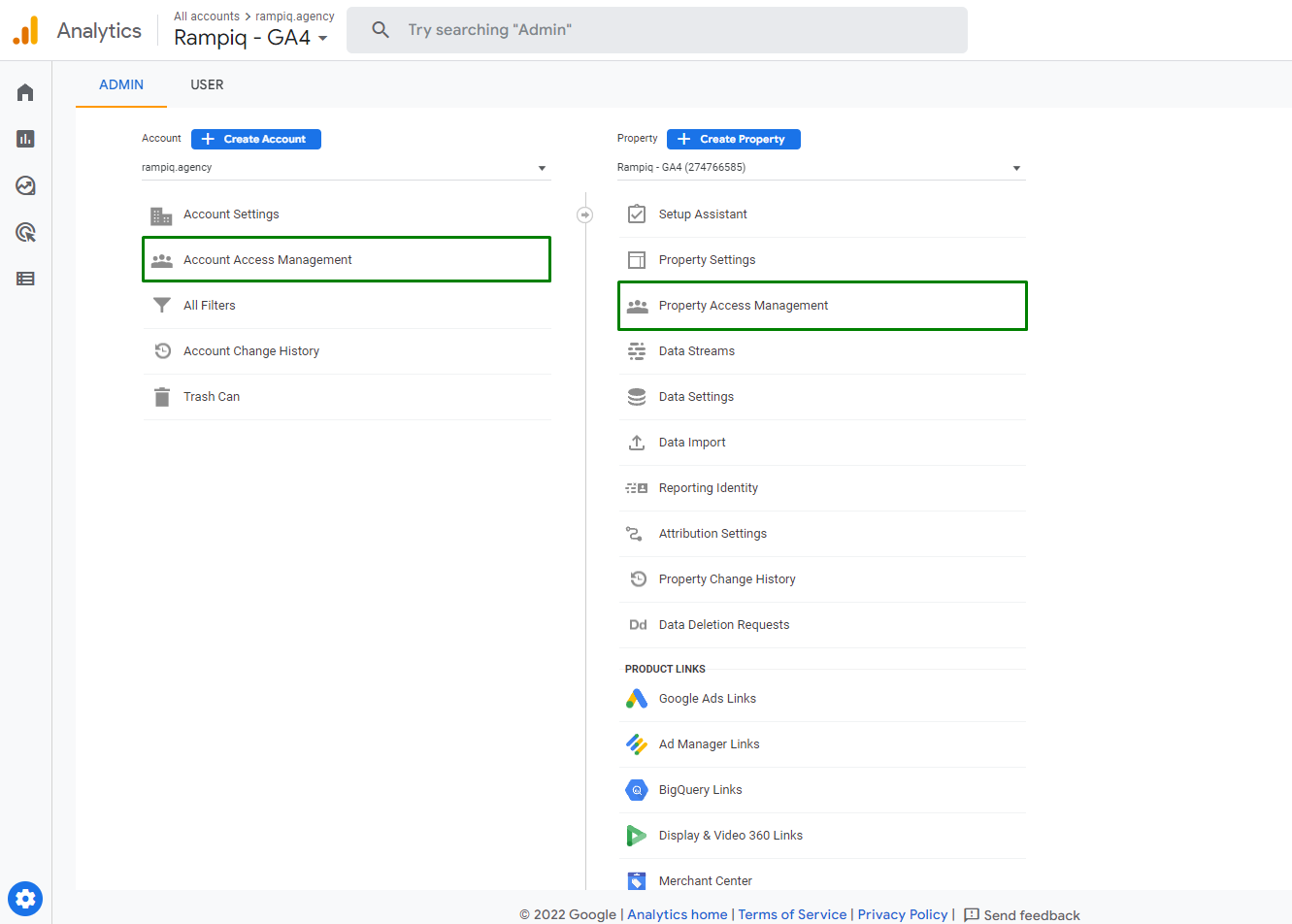
Step 2. Set up the GA4 Account and Install the Code
Creating a new GA4 property is the first step in the migration process. This involves setting up a new property in your Google Analytics account and configuring it to meet your specific tracking needs. We recommend using Google Tag Manager (GTM) for this step, instead of adding GA4 code to your source code.
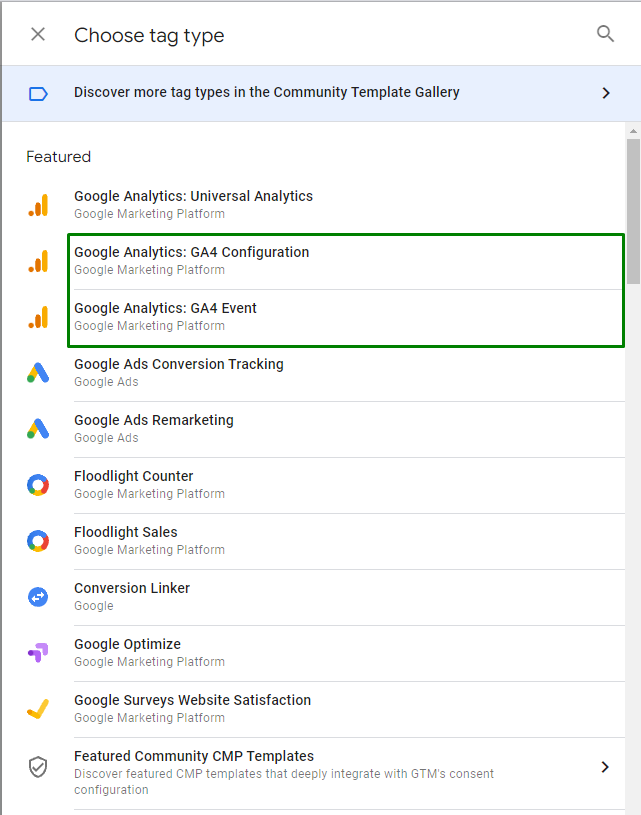
It is worth saying a few words about some advantages of GTM:
- Testing tools first of all. You can easily test all your tags before deploying them on the website in testing mode.
- You see all your marketing tags and everything that you have added to the site in one place. In addition, built-in syntax validation and templates greatly reduce the likelihood that the tag will simply not work.
- Fast Deployment: No need to involve developers or wait for the next release, just to add marketing tags (different pixels, conversions, audiences, tools, etc.)
- Versions, security, and user permissions: All published versions are saved separately, you can roll back to the previous version at any time, view the history of changes, and control who and when made changes. Also, assign users to different roles with different levels of access.
- Templates: GA4 has many templates to install your tags and tools. Found a new tool? Most likely this template will already be in GTM to install it, you just need to select it. Didn’t find a template? Simply use Custom HTML or templates built by the community.
And of course, it is worth saying that Google Tag Manager this is an absolutely free tool made by Google!
Step 3. Create and Launch GA4 Property with Necessary Data Streams
It is important to set up data streams from all environments you need to track, i.e. subdomains, apps, etc. In other words, you need to make sure you are collecting data from all resources you need to track your new GA4 property.
Step 4. Set Up Goals and Custom Events in GA4
We recommend setting up all important events and triggers using GTM, as this lets you keep all your GA4 settings in one place. GTM is a very flexible tool that can address 90% of the custom events setup. After setting up the events, you can then add goals to make sure that you can support your reporting infrastructure.
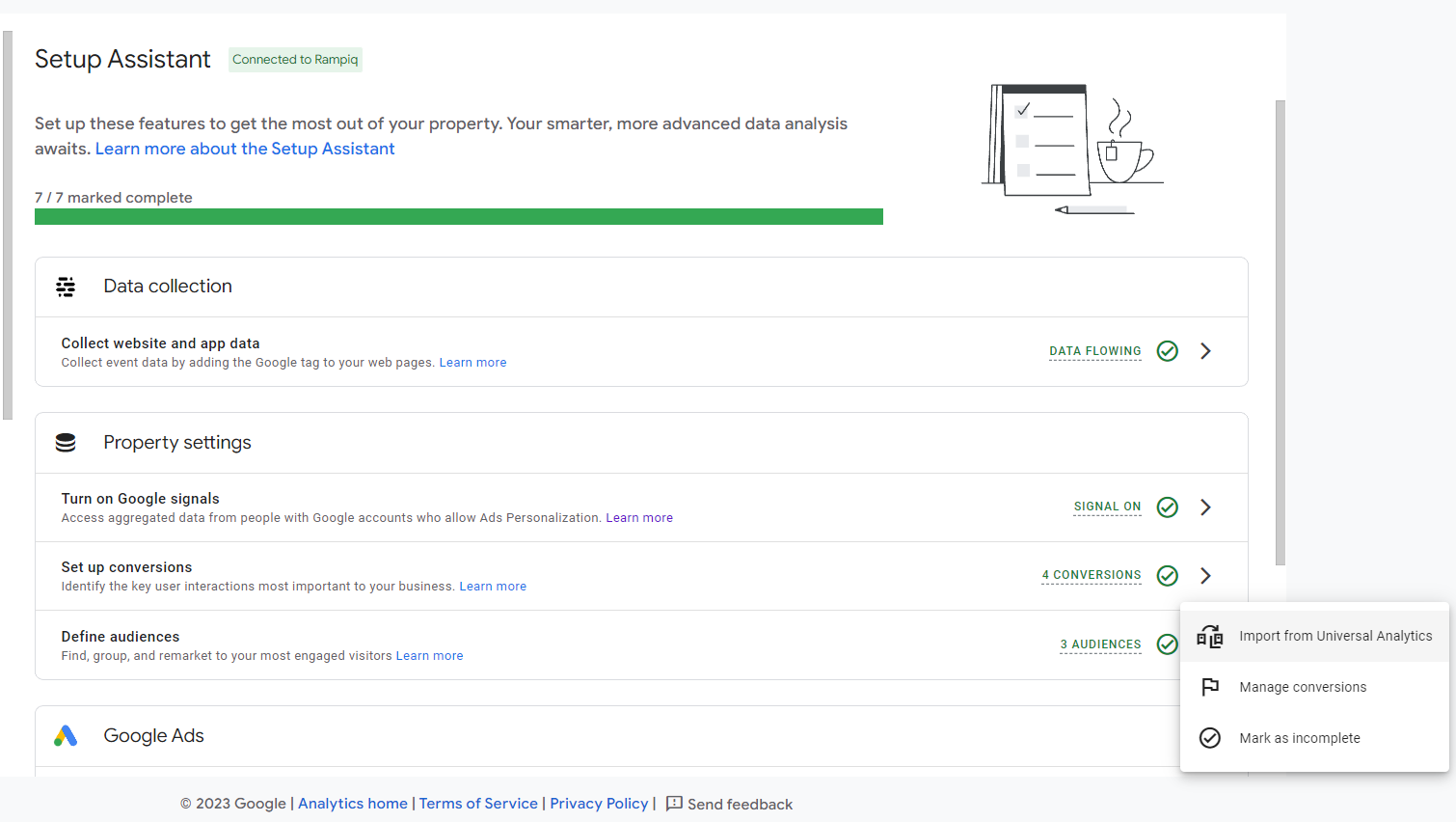 Note that although you can import some conversions from UA using the Setup Assistant tool, you must be careful and confirm that these events work. Do this because you need to fulfill a number of conditions to get them working.
Note that although you can import some conversions from UA using the Setup Assistant tool, you must be careful and confirm that these events work. Do this because you need to fulfill a number of conditions to get them working.
To avoid problems when for some reason these conversions on the site stop working at some point, we highly recommend setting up all the necessary events separately using a special template for GA4 events and using the event structure designed for GA4.
Please note that when setting up from scratch, using the special GTM template for GA4 events, you can add additional parameters to your event, set conditions and configure events as flexibly as you wish. Knowing that a single trigger for this event will work the way you want it to.
If you track an event not only in GA4, say in Facebook, LinkedIn, Bing Ads, Google ads, etc., you probably want to have one properly working trigger that will fire for this event and send data to all systems at once. This will help you avoid large discrepancies in the data, which can only increase due to the fact that different systems may use different attributions.
Step 5. Cross-Validate GA4 Data With Your Internal Systems
As Google Analytics 4 works differently from Universal Analytics in terms of data collection and processing, it is important to validate form submissions, purchases, registrations, and other business-critical data with your internal systems. Thus you will make sure that GA4 reports reflect your conversions correctly.
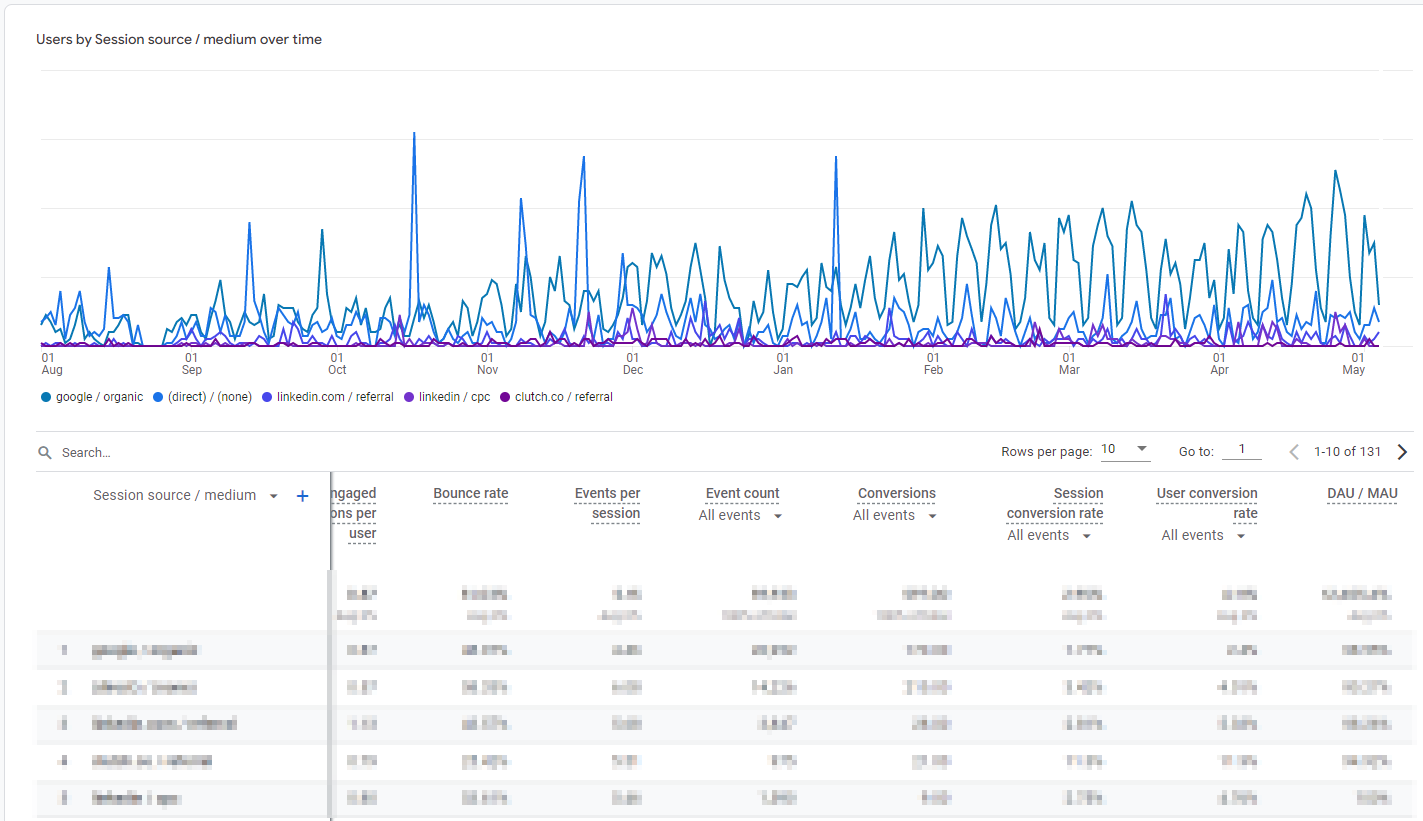
Step 6. Build Reports and Funnels
Apart from standard reports, GA4 offers robust custom reporting capabilities called Explorations. We recommend adding Explorations based on the most common business questions you need to address on a regular basis. We found User Lifetime and Segment Builder to be quite useful to set up right after you validate your GA4 data.
Step 7. Link Your GA4 Account to the Necessary Tools
Set up integrations with Google Ads, Google Search Console, and other supported systems.
Step 8. Plan a Date to Migrate GA4 as Your Sole Source
Finally, after making sure your new reporting system works properly, plan the final shutdown of Universal Analytics for your organization.
Step 9. Archive Your Universal Analytics data
Besides the forced migration to Google Analytics 4, Google announced that it will delete all Universal Analytics data beginning on January 1 2024. This means that you may want to download reports from your UA properties if you’d like to have access to your historical data after this date.
Google Ads Update
Since Universal Analytics properties will stop processing data from July 1, 2023, your conversions, audiences, and site statistics used in your Google Ads campaigns will no longer be updated.
To ensure that your campaigns continue to collect accurate data and work towards your conversion and business goals, we recommend taking the following steps.
Action plan:
- Set up Google Tag Manager (if applicable) for easy systems’ tags management.
- Check that all main GA4 conversions and remarketing audiences are set up correctly and imported to your Google Ads account.
- Set up a Google Ads tag and create conversion goals and remarketing audiences based on the tag to ensure all data is collected properly after July 1.
- Change your campaigns’ goal settings from GA UA to GA4 or Google Ads goals.
- Change your remarketing campaigns’ audience settings from GA UA to GA4 or Google Ads remarketing audiences.
If you have not used Google Ads Tag and Google Ads Conversions separately before, but only used imported conversions, then you have probably not maximized the effectiveness of your campaigns, as it could be done.
When do I Need to Migrate to GA4?
GA4 offers a range of new features and improvements over the soon-to-be-legacy Universal Analytics, such as more advanced tracking capabilities, deeper integration with Google Ads, and the ability to track user behavior across multiple devices. It gives you more valuable insights into your customer behavior and improves their overall digital strategy
Universal Analytics will stop collecting data in July 2023. However, we recommend that you migrate to GA4 early, as GA4 starts collecting data only since it’s set up on your website or app.
In other words, you can’t import your Universal Analytics data into GA4. Therefore, if you’d like to keep your historic website or app data in GA4, you need to install it as soon as possible.
What are the Key Differences Between GA4 and Universal Analytics?
- The way user data is collected: In GA4, every hit, or user interaction with your website, is an event. Compared to pageview-based tracking of Universal GA, this adds a ton of flexibility in how you can customize tracking based on your business needs. In addition to that, event-based analytics reduces data sampling, which is a big issue in Universal Analytics.
- Full-featured cross-device tracking: GA4 introduces full cross-device and cross-platform reporting. In GA4, you can combine a website data stream with an app data stream in one place and analyze how your users interact with both environments in one reporting space.
Machine Learning Features and Predictive Metrics
GA4 features an automated way to enrich your data with predictive models. Here are the predictive metrics you can get with GA4:
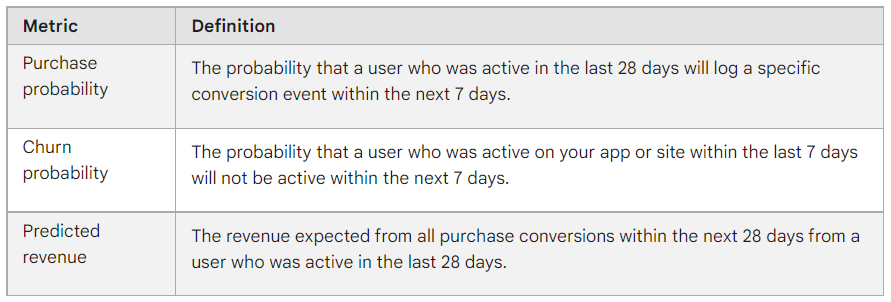 Source: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9846734
Source: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/9846734
With this data, you can build better audiences for your ads campaigns and use these metrics in User lifetime evaluations.
2 Critical Settings to Migrate to GA4
- Conversions. First and foremost, you need to make sure that you have your goals and conversions properly set up in GA4. This is important because you will use this data in your reports, and it’s vital that you migrate your settings early. You are likely to see the difference in conversions between GA4 and Universal Analytics due to the different ways conversions data is collected.
- Custom events. If you rely on custom events in your reporting, this is the part that you’d want to learn how to migrate to GA4. This will let you keep your data infrastructure very similar to what you have in Universal Analytics.




 Note that although you can import some conversions from UA using the Setup Assistant tool, you must be careful and confirm that these events work. Do this because you need to fulfill a number of conditions to get them working.
Note that although you can import some conversions from UA using the Setup Assistant tool, you must be careful and confirm that these events work. Do this because you need to fulfill a number of conditions to get them working.
 Source:
Source: 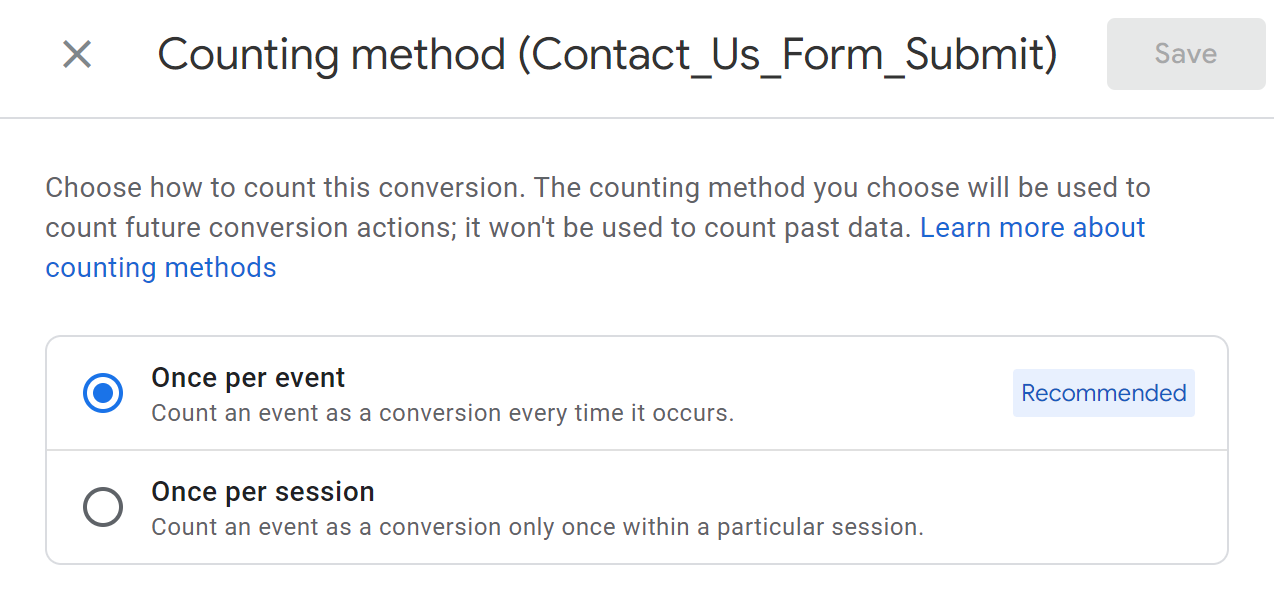 Let’s say you have several buttons that a user can click multiple times in a session and you don’t want to see all 10 button clicks as conversions. You should select the Once per session method to Count an event as a conversion only once within a particular session.
Let’s say you have several buttons that a user can click multiple times in a session and you don’t want to see all 10 button clicks as conversions. You should select the Once per session method to Count an event as a conversion only once within a particular session.